During my stay at the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), I had the opportunity to learn from the knowledgeable team and explore their suggestions. I had the chance to understand much more concerning the EBI and especially the European Genome-Phenome Archive (EGA). I will also be able to pursue a search on SMPC now that I had the chance to explore at the EBI. The next step would be to try working on a gene and search for genome-wide possibilities.
To help researchers learn about finding, accessing and analysing sensitive human data in a federated fashion, the CINECA project has developed a learning pathway. In this blog, we describe why federated data analysis is important, what is included in the learning pathway and how it can be accessed.
In the Passport is the glue between the researcher, data and computing blog post I introduced GA4GH Passports as an enabler of “the bring compute to data” paradigm. CINECA WP2 also contributed to GA4GH Passport standard for Digital identity and access permissions publication in Cell Genomics in autumn 2021.
The EUCAN Cluster consists of seven projects (CINECA, EUCANCan, EUCAN-Connect, euCanSHare, iReceptor Plus, and ReCoDID) that received funding under the same Horizon 2020 call, SC1-BHC-05-2018.
This document provides a high-level overview of each project in the cluster.
Recently WP4 has delivered a simple demonstrator pipeline to perform a federated joint variant genotyping analysis. The goal of this use case is to demonstrate how a simple metric (in this case, allele frequency) can be computed in a federated manner, without requiring ever collecting the individual level data in a central location.
This month’s blog was written by Nicola Mulder, Professor and head of the Computational Biology division at the University of Cape Town, and Principal investigator of H3ABioNet, a Pan African bioinformatics network for H3Africa, and Mamana Mbiyavanga, a Bioinformatics Scientist and PhD student at UCT, who contribute to a diverse range of CINECA work packages. This blog is less of a technical report in our Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH) standards series than the previous 4, and more of a report on how WP6 - ‘Outreach, training and dissemination’ is contributing to developing better implementation of GA4GH standards.
This month’s blog was written by Melanie Courtot, metadata standards coordinator at EMBL-EBI and co-Work Package Lead of CINECA WP3 - Cohort Level Metadata Representation. This blog is the fourth in our Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH) standards series, presenting an overview of how GA4GH standards are being developed and implemented by CINECA. In our April post about Passport, Mikael from CINECA WP2 explained the importance of controlled-access to protect sensitive data, federated data access in the cloud and how Passport enables researchers to authenticate - prove they are who they say they are.
This month’s blog was written by Mikael Linden, Senior application specialist at CSC - IT Center for Science, and co-Work Package Lead of CINECA WP2 - Interoperable Authentication and Authorisation Infrastructure. This blog is the third in our GA4GH standards series, presenting an overview of how GA4GH standards are being developed and implemented by CINECA. For the first blog in the series, giving a broad overview of how CINECA is facilitating federated data discovery, access and analysis, please see Dylan Spalding’s blog Implementation of GA4GH standards in CINECA.
This month’s blog was written by Lauren Fromont (CRG), a member of the EGA team at CRG and a member of CINECA WP1 - Federated Data Discovery and Querying. This blog is the second in our GA4GH standards series, presenting an overview of how GA4GH standards are being developed and implemented by CINECA.
This month’s blog was written by Dylan Spalding (EMBL-EBI), Coordinator of the European Genome-phenome Archive and co-WPL of CINECA WP4 - Federated Joint Cohort Analysis. This blog is the first in our new series, presenting an overview of GA4GH standards being developed and implemented by CINECA.
The final blog in our series on text-mining is a guest blog written by Shyama Saha, who specialises in Machine Learning/Text Mining at EMBL-EBI. The CINECA project aims to create a text mining tool suite to support extraction of metadata concepts from unstructured textual cohort data and description files. To create a standardised metadata representation CINECA is using Natural language processing (NLP) techniques such as entity recognition, using rule-based tools such as MetaMap, LexMapr, and Zooma. In this blog Shyama discusses the challenges of dictionary and rule-based text-mining tools, especially for entity recognition tasks, and how deep learning methods address these issues.
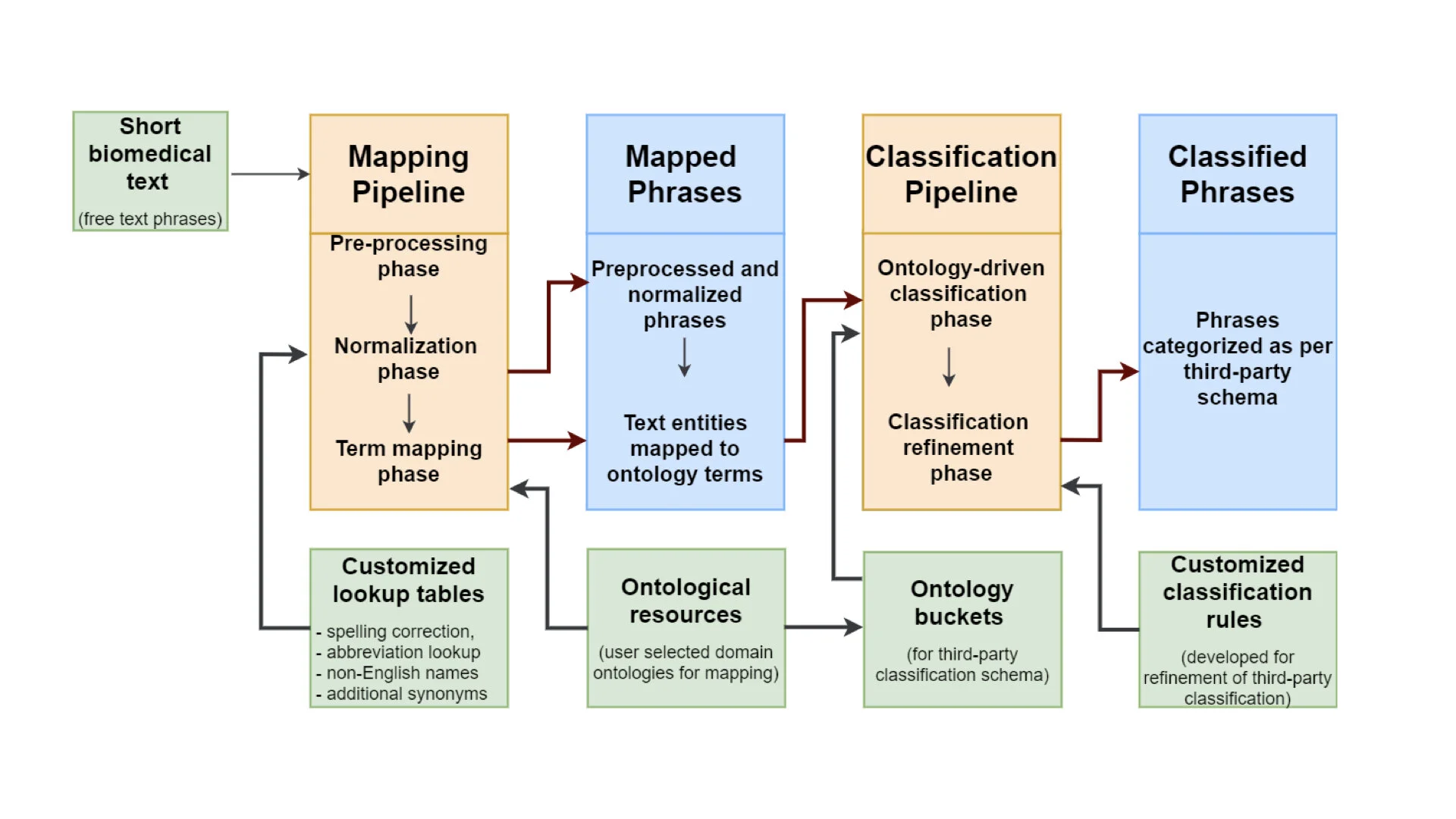
This post is part of a series on a text-mining pipeline being developed by CINECA in Work Package 3. In previous instalments, first, Zooma and Curami pipelines were explained in "Uncovering metadata from semi-structured cohort data". Then, LexMapr was introduced in "LexMapr - A rule-based text-mining tool for ontology term mapping and classification". In this third instalment we are going to explain the normalisation pipeline developed at SIB/HES-SO.
The initial focus of LexMapr development has been on providing a text-mining tool to clean up the short free-text biosample metadata that contained inconsistent punctuation, abbreviations and typos, and to map the identified entities to standard terms from ontologies. This blog is the second in a series on text-mining in CINECA. For the previous instalment "Uncovering metadata from semi-structured cohort data" please click here.
Harmonisation of attributes across different cohorts is very challenging and labour intensive, but critical to leverage the collective potential of the data. The CINECA text mining group aims to provide common tools and methods to extract additional metadata from structured and semi-structured fields in cohorts’ data.
Direct industrial participation in CINECA is made by the SMEs (Small and Medium-sized Enterprises) The Hyve and Clinicageno, both companies with an interest in bioinformatics applied to research and clinical genomic problems. The key background driver for their interest in a project like CINECA are the possibilities for long-term, sustainable profits in the areas of data-driven science and medicine in which the Hyve and Clinicageno specialise.
Gary Saunders is the Human Data Coordinator at ELIXIR. Gary leads the implementation of the ELIXIR-wide strategy to enable responsible sharing of human data consented for reuse in scientific research.
Meet the CINECA team and see the people behind the scenes as part of our Connect with CINECA series. Emma is a bioinformatics graduate student in the Molecular Biology and Biochemistry department at Simon Fraser University, Canada, under the supervision of Dr. Fiona Brinkman.
This work has contributed towards establishing a description of the trust model and four different levels of data access concerning specific cohort’s data, identifying use cases for the development of federated analysis workflows and describing existing data access models to inspire subsequent WP4 deliverables related to the implementation of the federated analysis workflow.
Meet the CINECA team and see the people behind the scenes as part of our Connect with CINECA series. Saskia is a bioinformatician and a PhD student working in metagenomics at the Erasmus Medical Centre in the Netherlands. Within the CINECA project she is co-Lead on Work Package 6 and a major contributor to Work Package 5.
Meet the CINECA team and see the people behind the scenes as part of our Connect with CINECA series. Aman is a member of the CanDIG team in Toronto, Canada, and a CINECA Work Package 2 contributor.
Meet the CINECA team and see the people behind the scenes as part of our Connect with CINECA series. Dr. Éloïse Gennet is a post-doc at the French national institute for health and biomedical research (INSERM).
The CINECA project wants to leverage on ELIXIR AAI to provide CINECA cohorts (that includes European, Canadian and African cohorts) with a way to integrate to ELIXIR AAI with their existing AAI approaches. This blog post briefly describes the process of integrating the ELIXIR and CanDIG AAI. A list of currently integrated services is also provided.
In order to facilitate collaboration and alignment between its different work packages, CINECA offers a staff visit program.
CINECA organised its first stakeholder engagement session at the International Cohorts Summit held in Reykjavík, Iceland in April 2019.

























In collaboration with other GA4GH-associated projects, CINECA is developing infrastructure which will permit effective use of widely-dispersed data increasing the size and quality of datasets available for disease research. In alignment with community standards, using standardised interfaces, data analysis will be federated and migrated to the data, respecting data access restrictions.
Solutions CINECA is adopting from the Discovery Work Stream include the Data Connect and Beacon v2 API, while from the DURI and Data Security Work Streams the GA4GH Passports, AAI and DUO are being utilised.